No. 84 Facile synthesis of self-healing gels using monochlorotriazinyl β-cyclodextrin
Summary
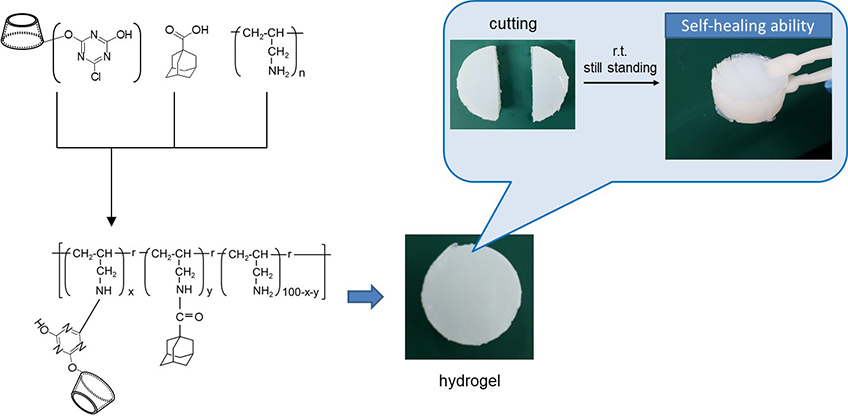
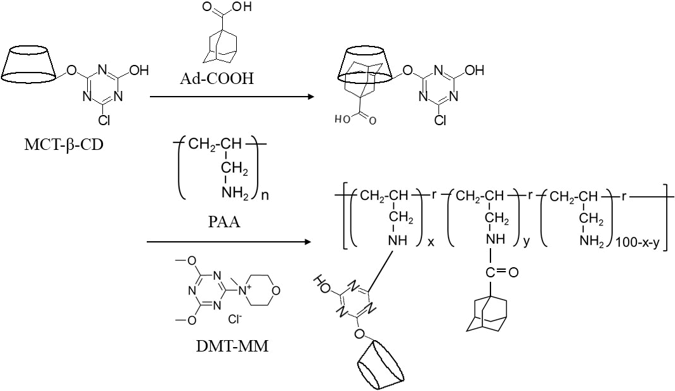
In recent years, self-healing gels have attracted attention to promote saving resource and energy. They are expected to be applied in a wide range of fields. Since the cross-linking bond in the gel formed by non-covalent host-guest interaction is reversible, it is possible to possess not only self-healing ability but also high toughness and impact absorption due to high internal viscosity. Self-healing gels using cyclodextrin (CD) as a host molecule have been well studied in recent years1,2). However, the synthesis of self-repairing gels reported to date requires a multi-step reaction. Therefore, by the use of commercially available monochlorotriazinyl-β-cyclodextrin (MCT-β-CD) as a host molecule and 1-adamantanecarboxylic acid (Ad-COOH) as a guest molecule, we have found a simple and economical method for synthesizing self-healing hydrogels by conjugating MCT-β-CD and Ad-COOH to polyallylamine (PAA).
Experimental
Ad-COOH was dissolved in MCT-β-CD aqueous solution. This solution was dropped into 15% PAA (average molecular weight 15,000) aqueous solution. Further, 2 molar equivalents of 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride (DMT-MM) to Ad-COOH were added.
The resulting reaction solution was allowed to stand overnight at room temperature to obtain a hydrogel (Fig. 1). It was confirmed that a hydrogel could not be formed from the same procedure by mixing MCT-β-CD, Ad-COOH and PAA without DMT-MM or mixing Ad-COOH, DMT-MM and PAA without MCT-β-CD.
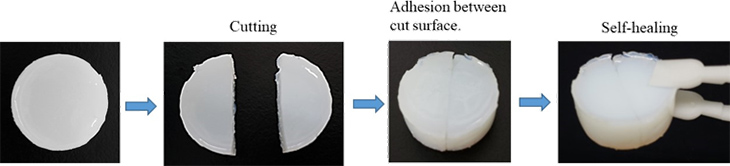
Next, the self-healing ability of hydrogel was examined. In addition, competitive experiments of host and guest molecules were performed to confirm host-guest interaction at the cut surface of the hydrogel. After the hydrogel was cut into half, one of the cut surfaces was soaked in 10 mM of β-CD solution as a competitive host molecule, or a 10 mM of Ad-COOH solution as a competitive guest molecule, or water without any host or guest molecules. Then re-adhesions between the cut surface without soaking and that with soaking were evaluated.
Results and discussion
A hydrogel could be easily formed by sequentially mixing MCT-β-CD, Ad-COOH, PAA and DMT-MM. The obtained hydrogel had self-repair ability in the readhesion test (Fig. 2). When the cut surface was soaked with Ad-COOH or β-CD aqueous solution, neither self-repair ability was shown. The mixture of MCT-β-CD, Ad-COOH and PAA without DMT-MM also became gelled. But its self-healing ability could not been shown. It is thought that these results indicate that the adhesion on the cut surface is due to host-guest interaction.
Conclusion
It was shown that hydrogels having self-repairing ability could be simply prepared by mixing commercially available reagents such as MCT-β-CD, Ad-COOH and PAA. This method is expected to be applied to the development of new industrial products in the future.
Reference
1) Akira Harada et al., Macromolecular., 37, 86-92 (2015).
2) Seunho Jung et al., Carbohydrate Polymer, 198, 563-574 (2018).
