No. 92 Dietary α-cyclodextrin induces anti-obesity effect
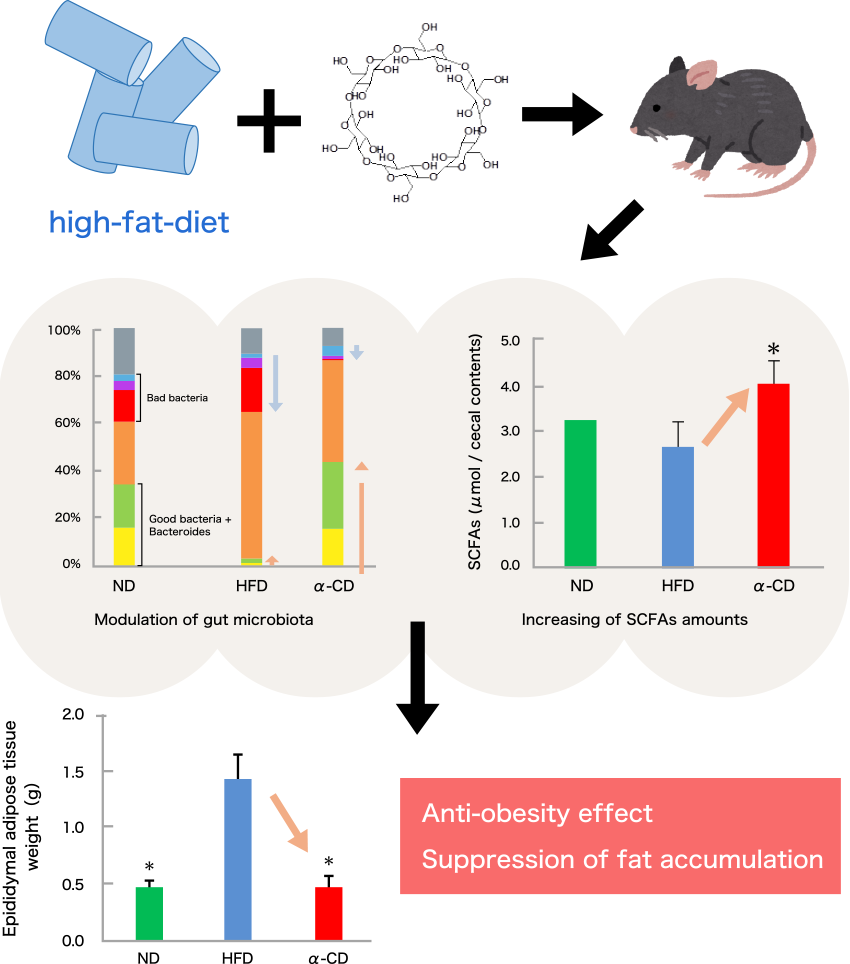
Summary
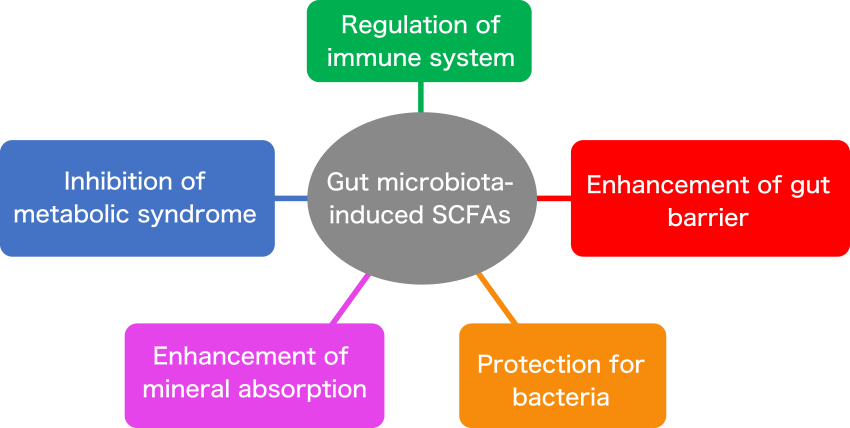
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) produced by gut bacteria from water-soluble dietary fiber induce various health promoting effects to the host (Fig. 1)1). Obesity is a risk factor for metabolic syndrome such as diabetes and high blood pressure, and it’s very important for obese-people to regulate body weight with dietary meals. Dietary fiber is known to have anti-obesity effect.
α-cyclodextrin (α-CD) is a water-soluble dietary fiber and has a fermentability by gut microbiota. We have previously reported that dietary α-CD modulates the gut microbiota and increases the amount of SCFAs in the cecum. (* For more details, please refer to the latest research results “85th” on our website.)
In this study, we investigated the effects of α-CD on obesity in mice fed a high fat diet.
Experimental methods
6-week-old male C57BL / 6J mice were divided into 3 groups: normal diet (ND) group, high-fat diet group (HFD), and high-fat diet + 5.5% α-CD diet (α-CD) group, and fed each diet for 16 weeks. After 16 weeks feeding, mice were sacrificed under anesthesia with isoflurane and then, cecum and epididymal fat were collected. SCFAs in the cecal contents were measured by GC-FID and fecal gut microbiota was analyzed by T-RFLP methods. Epididymal fat was weighed and analyzed with histological analysis and real-time PCR.
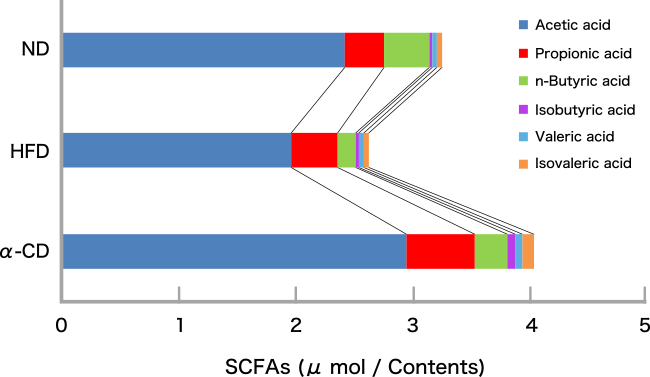
Results and discussion
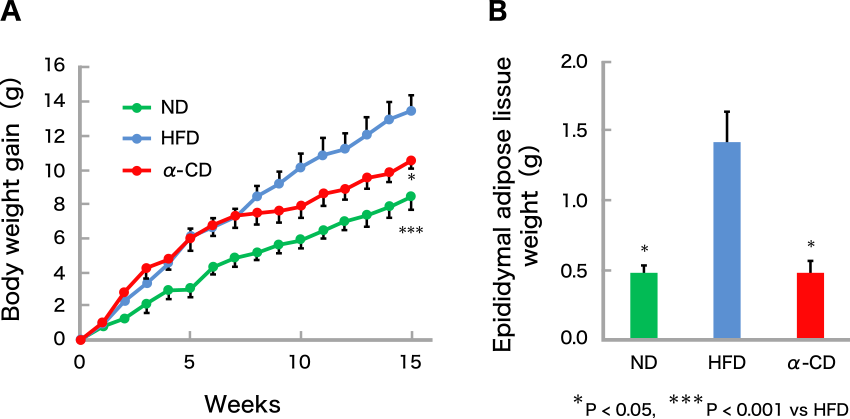
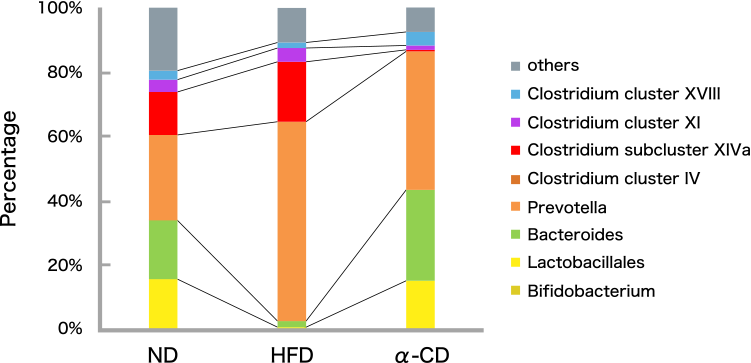
The body weight was significantly increased in the HFD group compared with the ND group. On the other hands, the increasing rate of body weight in the α-CD group was significantly lower than that in the HFD group (Fig. 2A). Epididymal adipose tissue weights of the a-CD group were also significantly lower than those of the HFD group (Fig. 2B). In addition, histological analysis revealed that the adipocyte size of epididymal adipose tissue in HFD group was larger than that in ND group, whereas the adipocyte size in αCD group was smaller than that in ND group. Additionally, gene expression in adipose tissue was significantly improved in the α-CD group compared to the HFD group. In the HFD group, the ratio of Bacteroides and good bacteria was lower compared with ND group, while in the α-CD group, the ratio of Bacteroides and good bacteria was higher and the ratio of bad bacteria was lower compared to the HFD group. (Fig. 3). The amount of SCFAs in the cecum was significantly increased in the α-CD group compared to the HFD group (Fig. 4).
Previous study reported that SCFAs in the gut promote the PPARγ gene that promotes fat miniaturization in adipose tissue2). Our results suggest that α-CD induces anti-obesity effect via increasing production of SCFAs.
Conclusion
The results of this study suggest that dietary α-CD have anti-obesity effect. In addition, α-CD is a very useful material to prevent the metabolic syndrome in the development of new health foods because it has the effects of reducing the amount of triglyceride and suppressing the rise in blood glucose levels after the meal.
(* For details, please refer to the latest research results "6th and 42nd" on our website.)
This research have been published in an international academic journal "Biofactors".
Nihei N et al., BioFactors, 44(4) :336-347 (2018)
Reference
1) Koh A et al., Cell, 165:1332-1345 (2016).
2) Kota BP et al., J. Clin. Invest. 101:1354–1361 (2005).
